Bronchitis is a common respiratory condition characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. It can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe respiratory distress. Understanding the symptoms of bronchitis is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
What Is Bronchitis?
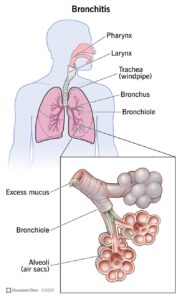
Bronchitis is a respiratory condition that occurs when the bronchial tubes become inflamed due to infection or irritation. It can be acute or chronic and is often accompanied by coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
Types of Bronchitis
There are two main types of bronchitis: acute and chronic. Acute bronchitis is typically caused by viral infections, such as the common cold or flu, and usually resolves within a few weeks. Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, is a long-term condition often associated with smoking or exposure to air pollution.
Causes of Bronchitis
Bronchitis can be caused by various factors, including viral and bacterial infections, environmental irritants, and underlying health conditions such as asthma or COPD. Smoking is the leading cause of chronic bronchitis.
Common Symptoms of Bronchitis
The symptoms of bronchitis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include coughing, wheezing, chest discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, and mucus production.
Acute Bronchitis Symptoms
Acute bronchitis typically starts with a dry or productive cough, which may be accompanied by fever, chills, sore throat, and body aches. In some cases, acute bronchitis can progress to pneumonia, especially in older adults or people with weakened immune systems.
Chronic Bronchitis Symptoms
Chronic bronchitis is characterized by persistent coughing and mucus production for at least three months out of the year, for two consecutive years. Other symptoms may include wheezing, shortness of breath, and frequent respiratory infections.
When to See a Doctor
It’s essential to see a doctor if you experience severe or persistent symptoms of bronchitis, such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, or coughing up blood. Additionally, seek medical attention if you have a weakened immune system or underlying health conditions.
Diagnosis of Bronchitis
Diagnosing bronchitis typically involves a physical examination, a review of your medical history, and possibly tests such as chest X-rays, lung function tests, or sputum culture.
Treatment Options for Bronchitis
Treatment for bronchitis depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. In most cases, treatment involves rest, hydration, over-the-counter medications to relieve cough and fever, and sometimes antibiotics for bacterial infections.
Home Remedies for Bronchitis Symptoms
In addition to medical treatment, there are several home remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms of bronchitis, including staying hydrated, using a humidifier, practicing breathing exercises, and avoiding irritants such as smoke and air pollution.
Prevention of Bronchitis
To reduce your risk of bronchitis, it’s essential to practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and quitting smoking. Additionally, getting vaccinated against the flu and pneumonia can help prevent bronchitis.
Complications of Bronchitis
While most cases of bronchitis resolve on their own with proper treatment and rest, complications can occur, especially in vulnerable populations such as older adults or people with underlying health conditions. Complications may include pneumonia, respiratory failure, or exacerbation of underlying lung conditions.
Living with Bronchitis
Living with bronchitis may require lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking, avoiding respiratory irritants, and staying vigilant about respiratory infections. It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to manage your symptoms and minimize the risk of complications.
Conclusion
bronchitis is a common respiratory condition characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes. Understanding the symptoms of bronchitis and seeking prompt medical attention when necessary is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
FAQs
- Can bronchitis be contagious?
Yes, bronchitis can be contagious, especially if it is caused by a viral infection. It is essential to practice good hygiene, such as covering your mouth when coughing or sneezing, to prevent the spread of infection.
- Is bronchitis the same as pneumonia?
No, bronchitis and pneumonia are two different respiratory conditions. While both can cause coughing and difficulty breathing, pneumonia typically involves inflammation and infection of the lung tissue, whereas bronchitis affects the bronchial tubes.
- Can bronchitis go away on its own?
Yes, acute bronchitis caused by viral infections usually resolves on its own within a few weeks with rest and supportive care. However, chronic bronchitis may require long-term management and treatment to control symptoms.
- Is bronchitis more common in smokers?
Yes, smoking is a significant risk factor for developing chronic bronchitis. Smoking damages the lining of the bronchial tubes and increases the risk of respiratory infections, leading to chronic inflammation and mucus production.
- Can bronchitis cause breathing difficulties?
Yes, bronchitis can cause breathing difficulties, especially if the airways become inflamed and narrowed. Shortness of breath, wheezing, and chest tightness are common symptoms of bronchitis, particularly during physical activity or exacerbations of the condition.