SYPHILIS: SYMPTOMS, PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
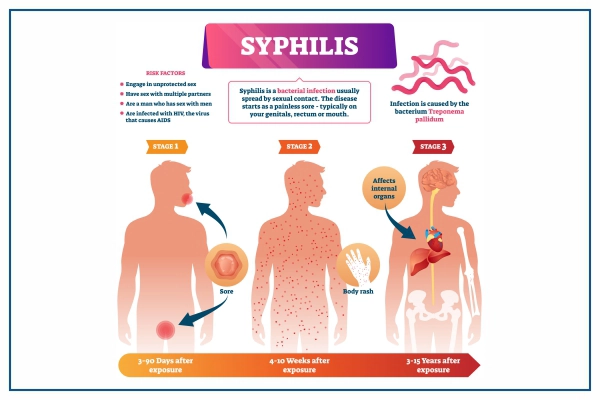
Diseases that are transmitted through direct sexual contact (including penis to vagina, penis to anus, mouth to genitals) are called STDs include a variety of diseases; Syphilis is one of them: Syphilis: It is a bacterial infection which usually spread through sexual contact of two persons. The disease initially presents as painless ulcers, usually on the genitals, rectum, or mouth. Syphilis is spread from person to person through skin or mucous membrane contact with these ulcers. After the initial infection, the syphilis bacteria may lie dormant (dormant) in your body for decades before reactivating. Syphilis can be cured in early stage, with a one injection of penicillin. If left untreated, syphilis can seriously damage your heart, brain, or other organs, and can be life-threatening. Syphilis can also be passed from mother to unborn child.
Symptoms
Syphilis develops in stages, and the symptoms of each stage vary. But stages can overlap, and symptoms don’t always appear in the same order. You can have syphilis for years without showing any symptoms.
Primary Syphilis
The first sign of syphilis is a small ulcer called a chancre. Usually occurs where bacteria enter the body. While most people with syphilis develop only one chancre, some patients may develop multiple. A chancre usually appears about three weeks after exposure to the germs. Many people with syphilis don’t notice a chancre because it’s usually painless and can hide in the vagina or rectum.
Secondary Syphilis
Within a few weeks of the chancre healing, a rash may appear that starts on the trunk and eventually spreads all over the body, even the palms and soles of the feet. This rash is usually not itchy and may be accompanied by warty sores on the mouth or genitals. Some people also experience hair loss, muscle pain, fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. These signs and symptoms may disappear within a few weeks or recur over a period of up to a year.
Latent Syphilis
If you do not receive treatment for syphilis, the disease transitions from the second stage to the latent (hidden) stage, which is temporarily asymptomatic. The incubation period can take several years to last. Symptoms and signs may not recur, or the disease may progress to stage III.
Tertiary Syphilis
About 15% to 30% of people with untreated syphilis develop the complication of late (tertiary) syphilis. In advanced stages, the disease can damage your brain, nerves, eyes, heart, blood vessels, liver, bones and joints. These problems can occur many years later if the initial infection is left untreated.
Neuro syphilis
Syphilis is transmissible at any stage and causes damage to the brain and nervous system (neurosyphilis), the eyes (ocular syphilis), and other damage.
Congenital Syphilis
Women with syphilis can pass the disease to their children through the placenta or during childbirth. Most newborns with congenital syphilis have no symptoms, although some newborns develop a rash on the palms and soles of the feet. Follow-up symptoms and signs may include deafness, tooth deformities, and a saddle nose (collapsed bridge of the nose). But babies born with syphilis can also be born prematurely, die at birth (stillbirth), or die after birth.
Prevention Method
Practice safe sex is the best way to reduce your risk of syphilis:
- Have an exclusive sexual relationship with an uninfected partner.
- Use condoms correctly. However, if syphilis lesions appear in other parts of the body, condoms cannot provide absolute protection.
Treatment Method
Syphilis is controlled as long as you’re taking antibiotics and complete the course of Syphilis treatment in stage one or two. You must have a blood test after treatment to make sure recovery. You and your sexual partner have to avoid sexual contact and wait till two weeks when finishing the course of treatment before returning to sex. The course of antibiotics for syphilis could also be longer. Whether your sexual partner wants treatment depends on the exposure and infection, please discuss this along with your doctor.
How To Save Yourself
Syphilis is a serious disease that affects the whole body, so patients must be treated thoroughly. Don’t do things on your own that could damage your or your partner’s health. If you suspect that you have syphilis, you must seek Medical Treatment.







